Norland Potato Fact Sheet

| Norland (ND2908-1R) |
 |
Parentage – Redkote x ND626
Breeder – North Dakota Agricultural College; released for production – 1957
Maturity – Early
Usage – Primarily used for the fresh market and home gardens; very good for boiling, frying, chipping (best at harvest), and fair for baking
Plant – Medium large, spreading; stems medium thick, prominently angled
Leaves – Dark green, glossy, medium large; slightly cupped and moderately close; secondary and tertiary leaflets are numerous
Flowers – Purple; orange anthers; few; green buds; red abscission ring on pedicel; gravity is low to intermediate (www.potatoassociation.org)
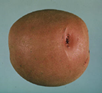
Tubers – Oblong, slightly flattened, smooth; red in color with shallow eyes; low to intermediate specific gravity and yields (www.potatoassociation.org) **Note –Red Norland, Dark Red Norland and New Red Norland are all selected clones of Norland that are of a darker red skin color.
Strengths – Seldom produces tubers the are irregular in shape, knobby or growth cracked; stores well; tubers are not subject to internal defects like hollow heart, internal necrosis and vascular discoloration; highly resistant to PVA; moderately resistant to common scab, potato wart, and Rhizoctonia (www.inspection.gc.ca)
Weaknesses – Sensitive to drought; susceptible to skinning and bruising if harvested before maturity; susceptible to black leg, Fusarium dry rot, early and late blight, leaf roll, Phoma rot, seed-piece decay, Verticillium wilt, PVX, and PVY; highly susceptible to silver scurf (www.inspection.gc.ca)

Photos provided by CFIA; Virus photos provided by www.potatovirus.com. For more information: www.potatoassociation.org or www.inspection.gc.ca
Last Revised: 8/23/2017
© 2017 The Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System
This article was posted in Fact Sheet.